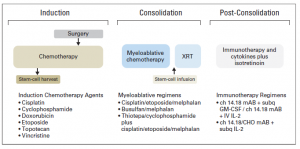
Children with high-risk neuroblastoma is the most challenging group to treat. Current treatment strategy for this group consists of 3 treatment blocks:
- induction: chemotherapy and primary tumour resection;
- consolidation: high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem-cell rescue and external-beam radiotherapy [XRT];
- post-consolidation: anti–ganglioside 2 immunotherapy with cytokines and cis-retinoic acid.
Pinto NR, Applebaum MA, Volchenboum SL, Matthay KK, London WB, Ambros PF, Nakagawara A, Berthold F, Schleiermacher G, Park JR, Valteau-Couanet D, Pearson AD, Cohn SL. Advances in Risk Classification and Treatment Strategies for Neuroblastoma.J Clin Oncol. 2015 Sep 20;33(27):3008-17.